Figge-Fencl Quantitative Physicochemical Model
of Human Acid-Base Physiology (Version 3.0)
by James J. Figge, MD, MBA
Copyright 2003 - 2026 James J. Figge.
Data Archive: Carbon Dioxide System.
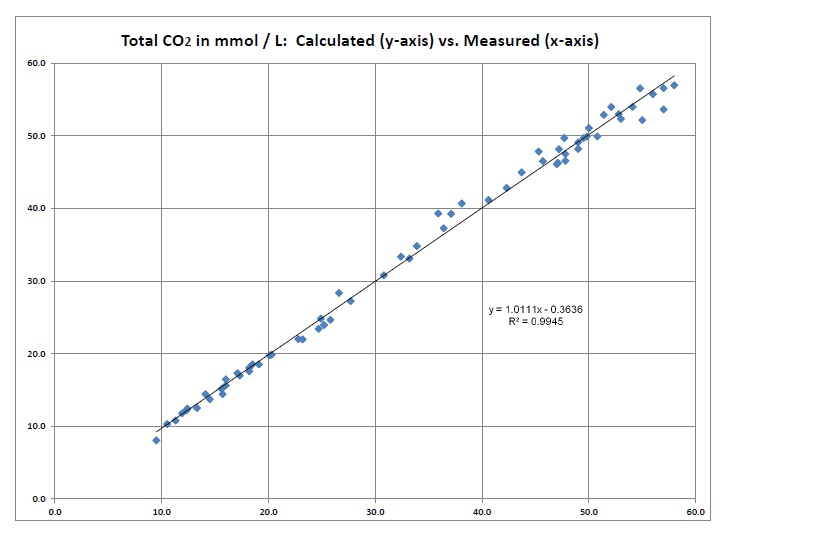
Figure 1. Calculated total CO2 versus measured total CO2.
This analysis serves as an internal check
of the validity of the constants for the CO2 system as employed in the Figge-Fencl Model. Slope =
1.0111. R2 = 0.9945. N = 65. Mean difference = 0.011. Standard Deviation = 1.20.
Total CO2 was directly measured in the data set of Figge, Rossing, and Fencl using gasometry [1].
Total CO2 can also be calculated from the measured pH and PCO2 in the same data set using constants
from the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
pH = 6.10 + Log10 ( [ HCO3- ] / ( 0.0307 x PCO2 ) );
where [ HCO3- ] is in mmol / L; and PCO2 is in Torr.
The constant Kc1, governing the carbon dioxide - bicarbonate equilibrium, is derived
directly from parameters in the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. The solubility of
CO2 in plasma is: 0.230 mmol / L / kPa x 0.13332236842105 kPa / Torr =
0.0307 mmol / L / Torr.
Kc1 = (10-6.10) x (0.0307) / (1000) = 2.44E-11;
the units for KC1 are (mol / L )2 / Torr.
Hence, it can be shown algebraically that calculations using Kc1 in the Figge-Fencl model yield results identical to those
calculated with the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
The constant Kc2, the second dissociation constant for carbonic acid, is calculated
from the formula (equation 9) given by Harned and Scholes [2]. At 37 degrees
Celsius (310 K), the formula yields: log Kc2 = (-2902.39 / 310) + 6.4980 - (0.02379 x 310)
= -10.239. Hence, at zero ionic strength, pKc2 = 10.239. The correction factor for an
ionic strength of 0.15 M is approximately 0.022. Hence pKc2 = 10.261, and kc2 = 5.5E-11 mol / L
(note: the value of Kc2 when expressed in Eq / L is 1.1E-10).
[ HCO3- ] = Kc1 x PCO2 / (aH+);
[ CO32- ] = Kc1 x Kc2 x PCO2 / (aH+)2;
dissolved CO2 and carbonic acid = 0.0307 x PCO2;
total CO2 = 1000 x [ HCO3- ] + 1000 x [ CO32- ] +
dissolved CO2 and carbonic acid;
where [ HCO3- ] is in mol / L;
[ CO32- ] is in mol / L;
dissolved CO2 and carbonic acid is in mmol / L;
and total CO2 is in mmol / L.
References:
1. Figge J, Rossing TH, Fencl V. The role of serum proteins in acid-base equilibria.
J Lab Clin Med. 1991; 117: 453-467.
2. Harned HS, Scholes SR. The ionization constant of HCO3- from
0 to 50 Degrees. J Am Chem Soc. 1941; 63: 1706-1709.


